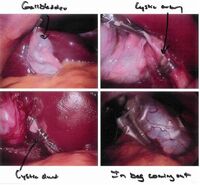
Cholecystectomy as seen through a laparoscope
Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive surgery (MIS), bandaid surgery, keyhole surgery, or pinhole surgery is a modern surgical technique in which operations in the abdomen are performed through small incisions (usually 0.5-1.5cm as compared to larger incisions needed in traditional surgical procedures.
Instruments
Electrosurgical devices are commonly used in laparoscopic procedures. The key element in laparoscopic surgery is the use of a laparoscope.
Laparoscope
A laparoscope consists of a telescopic rod lens system, that is usually connected to a video camera.
Carbon dioxide gas
The abdomen area is usually insufflated. Therefore carbon dioxide gas is used to create a working and viewing space.
This gas. is common to the human body and can be absorbed by tissue and also removed by the respiratory system.
Properties
Carbon dioxide gas is important because the abdomen is essentially blown up like a balloon (insufflated), elevating the abdominal wall above the internal organs like a dome.
It is also non-flammable, which is important because of the electrosurgical devices which are commonly used in laparoscopic procedures.
Cable connection
Electrosurgical devices are attached to a fiber optic or Optical fiber cable, where ever required.
The system also is connected to a 'cold' light source (halogen or xenon), to illuminate the operative field, inserted through a 5 mm or 10 mm cannula or Trocar to view the operative field.
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). | 
|